DAO and Service Layer for CRUD operation.
In the Part 4 article, we have seen how to integrate spring and hibernate. Now we create the DAO and service layer for the CRUD Operation.
Step 1:
First the Delete Package named “CRUDExample” which is created by default. Now Select “Java” folder and right click, Select New –> Other-> Package and enter the Package name as “crudexample.dao” as shown.

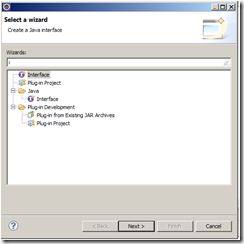
Select the “dao” package, right click, select New –> Other->Interface as shown here
Enter the interface name as “CRUDDao” as shown.
We will write our DAO interface as generic, so that in the future we can use for any CRUD screen.
package crudexample.dao;
import java.util.List;
public interface CRUDDao {
<T> List<T> getAll(Class<T> klass);
<T> T save(T t);
<T> void delete(T t);
}
Step 2:
Next we will create CRUDDao implementation class which will implement the above interface.
Select the “dao” package, right click, select New –> Other->class and enter the class name as CRUDDaoImpl.java


Here is the java class code.
package crudexample.dao;
import java.util.List;
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
import javax.persistence.PersistenceContext;
import javax.persistence.PersistenceContextType;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class CRUDDaoImpl implements CRUDDao {
@PersistenceContext(type = PersistenceContextType.EXTENDED)
private EntityManager em;
public EntityManager getEm() {
return em;
}
public void setEm(EntityManager em) {
this.em = em;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> List<T> getAll(Class<T> klass) {
return em.createQuery("Select t from " + klass.getSimpleName() + " t")
.getResultList();
}
public <T> T save(T t) {
T newRecord = null;
newRecord = em.merge(t);
return newRecord;
}
public <T> void delete(T t) {
em.remove(em.merge(t));
em.flush();
}
}
Step 3:
Next we will create our service layer. Now Select “Java” folder and right click, Select New –> Other-> Package and enter the Package name as “crudexample.service” as shown.

Select the “service” package, right click, select New –> Other->Interface as shown here
Enter the interface name as “CRUDService” as shown.
Here is the interface code
package crudexample.service;
import java.util.List;
public interface CRUDService {
<T> List<T> getAll(Class<T> klass);
<T> T save(T t);
<T> void delete(T t);
}
Step 4:
Next we will create CRUDServiceImpl implementation class which will implement the above interface.
Select the “service” package, right click, select New –> Other->class and enter the class name as CRUDServiceImpl.java

Here is the Class code
package crudexample.service;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import crudexample.dao.CRUDDao;
@Service
public class CRUDServiceImpl implements CRUDService {
@Autowired
private CRUDDao CRUDDao;
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public <T> List<T> getAll(Class<T> klass) {
return CRUDDao.getAll(klass);
}
@Transactional
public <T> T save(T t) {
T newRecord = null;
newRecord = CRUDDao.save(t);
return newRecord;
}
@Transactional
public <T> void delete(T t) {
CRUDDao.delete(t);
}
}
Step 4:
Next we will domain object for appusers table in the database. Select “crudexample” package, right click, select new-> other->Package and enter the package name as”domain”
Now select the package “domain”, right click, select new-Other->Class and enter the class name as “Appusers”
Here is the code for the same.
package domain;
import java.io.Serializable;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
@Entity
public class Appusers implements Serializable {
/**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private long id;
private String firstName;
private String userID;
private String lastName;
private String password;
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
public String getUserID() {
return userID;
}
public void setUserID(String userID) {
this.userID = userID;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(long id) {
this.id = id;
}
}
That’s all. In the next article, we will create our Presentation layer using ZK Framework.![]()
![]()
![]()

















0 comments:
Post a Comment